COM-1S and COM-2S
Features
- COM-2S: Two independent, completely configurable, serial ports
- COM-1S: One, completely configurable, serial port
- Supports conventional RS232, High-speed RS-422, and Multi-drop RS-485
- Supports all standard RS-232 lines: TD, RD, RTS, CTS, DCD, DTR, and DI
- Can be wired for 2 or 4 wire RS-422/485 communications
- Supports RS-485 handshaking on-board without special drivers to support Windows and non-DOS programs
- Built-in support for local echo, line termination, and line bias supplies
- Supports extended AT interrupts
- LED status monitors on transmit and receive lines for troubleshooting
- Designed, made, supported, and manufactured in the USA
Price range: $169.00 through $269.00
In StockDescription
The dual-port COM-2S and single-port COM-1S cards can be used in ISA Bus computers. They support all of the popular communication protocols. RS-232 communication is fine for short distances and development work. RS-422 adds differential drivers and extends the distance. And RS-485 communication uses tri-state drivers to produce a multi-drop network capability for up to 32 ports on a single twisted pair.
The cards have type 16550 buffered UART’s and are compatible with MS-DOS and multitasking operating systems. I/O bus address is set up by DIP switches on the card and address is not limited to just COMx addresses. Continuous address selection is available anywhere in the I/O address range 100 to 3F8 (hex). Interrupt levels IRQ2 through IRQ14 (except IRQ8, 9, and 13) are supported. A crystal-controlled oscillator is located on the card. This oscillator permits precise selection of baud rate from 50 to 115,000 baud. Higher baud rates are optionally possible using a different UART and higher crystal frequency. The transceiver used, a type 75176, is capable of driving extremely long communication lines at high baud rates. It is capable of driving up to 60 mA on balanced lines and receiving inputs as low as 200 mV differential signal super imposed on common mode noise of maximum -7V to +12V. Also, in case of communication conflict, the transceivers feature thermal shutdown.
In addition to differential Transmit and Receive lines, single-ended, buffered RTS and CTS lines are provided at the I/O connector. Normally, CTS must be pulled up to +5 VDC for the card to operate but you can position a jumper so that the COM-2S will auto-detect the transition between transmit and receive operations. The COM-2S supports full duplex, half duplex and simplex operations selected by jumpers.
RS-485 multidrop communications requires the transmitter drivers to be enabled and disabled as needed to allow the ports to share the common communications lines. The COM-2S card has two methods to control the drivers: automatic (AUTO) and Request to Send (RTS) control. Under automatic control, the port is normally in the receive mode and the driver is enabled only when data is ready to be transmitted. The driver is then enabled and remains enabled throughout transmission plus the transmission time of one character after data transfer is complete. Then it is disabled. The COM-2S automatically adjusts its timing to the baud rate of the data. When operating with Windows programs, this AUTO mode is mandatory. With RTS control, your application software must enable/disable the driver.
A transmission line should be terminated at the receiving end in its characteristic impedance in order to eliminate “ringing.” You can install jumpers that apply a 120ohm and 0.1 µF capacitive load across the input for RS-422 mode and across the transmit/receive input/output for RS-485 operation. In RS-485 operations, where there are multiple terminals, only the RS-485 ports at each end of the network should have terminating resistors. Also, for RS-485 operation, there must be a bias on the RX+ and RX- lines. If the COM-2S card is to provide that bias, you can install jumpers at the two locations labeled BIAS.
OPTIONS
- Tranzorbs to absorb potentially damaging voltage spikes occurring due to lightning or other transmitted electrical interference.
- High-speed crystal oscillators to achieve higher baud rates.
Modified-COTS (MCOTS) Customization
ACCES can tailor any standard product to your precise requirements — electrical, mechanical, firmware, environmental, or connector-level. Common MCOTS options include alternate I/O ranges, isolation enhancements, firmware changes, private labeling, conformal coating, extended temperature operation, ruggedized enclosures, and military-grade components. If this product is close but not a perfect fit, our engineering team can deliver a rapid-turn MCOTS variant with minimal NRE and dependable, Made-in-USA quality.
Downloads
Manuals
Software
- COM-1S Software Package ( -- Last Uploaded 2025-05-07)
- COM-2S Software Package ( -- Last Uploaded 2025-05-07)
Drivers and Downloads
Full list of available Downloads: Software Packages, Drivers, Manuals, and other documents
Information about our Free Software packages:
ACCES is proud to provide a full suite of software support with every Data Acquisition product. We are committed to supporting the most popular operating systems and platforms for our customers. Currently we are actively supporting 7 -> 11, both 32 & 64 bit, including “Server 2008,” “Embedded,” and “Compact” flavors for all plug-and-play products including PCI, PCI Express, USB, and more. Many products continue to ship with support for additional operating systems such as DOS, Windows 95, 98, Me, NT4, 2000, and XP.
Samples
Among the software we deliver with our products are sample programs in a wide variety of programming languages. These samples are used to demonstrate the software interfaces to our products — and many can be used as-is in your production environments, or to test functionality of the devices out-of-the-box. We’re currently actively supporting sample programs in Microsoft Visual C#, and Delphi, with many devices including samples in Visual Basic (5 and .NET), Visual C/C++, and Borland C/C++ 3.1 for DOS. Additionally we provide National Instruments LabVIEW compatible DLLs and many demonstration VIs for our devices.
Drivers
Drivers for various operating systems are also provided, including active support for Windows 7 -> 11 — all in both 32-bit and 64-bit flavors, and including consumer, server, and embedded varieties — as well as the 2.6 and newer Linux kernels and recent OSX / macOS versions. Many products continue to ship with driver support for Windows 95, 98, Me, NT4, Windows 2000, XP, and more, but support for these operating systems is considered deprecated.
Setup Programs and Utilities
Our Data Acquisition devices also include a graphical setup utility that walks you through the process of configuring any option jumpers or switches on the device, as well as explaining a little about the various connectors present.
Many devices also include utility programs – little tools to make your use of the device easier, such as EWriter, a program that allows you to read and write data in the user-accessible EEPROM locations on all our USB data acquisition products; or WinRISC, a “Really Incredibly Simple Communications” terminal program that lets you get started instantly with serial devices.
“Register Level” Documentation
Besides all this software in all these languages and operating systems ACCES has a policy of open and transparent development: none of our lowest-level “register” interfaces are hidden from you — we document every register in every bus card, every command in every serial board, and every usb control transfer in every USB Data Acquisition board. These lowest-level interfaces allow you to develop for our products in ANY operating system or language, regardless of our actively supporting it or having a driver for it. We have customers actively developing in ADA, Android, Python, Java, MATLAB, Solaris, and more, just by referring to our complete low-level interface documentation! And we provide the full source code to all of our drivers, regardless of operating system, to give you an even bigger head start in your own development tasks.
No Fees or Royalties
All of this software is provided at no additional charge, and is licensed under any of a variety of flexible — and royalty free — options. Check out our software license explanation if you’d like more information.
Custom Software
ACCES also offers Custom Software Services for our products. Our prices are unbelievably low, often as inexpensive as free! If you need something tweaked to support your needs, or an entire enterprise application developed from scratch, it is definitely worth your time to inquire with us, first.
Further information about available ACCES Software:
Redistributing Windows Drivers
A list of ACCES drivers and the files that compose them under different versions of Windows, so you can easily redistribute ACCES cards and drivers.
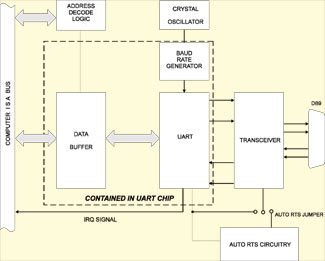
Note: only one serial port shown
Communications Interface
- Serial Ports: One or Two shielded male D-sub 9-pin connectors compatible with RS-232, RS-422 and RS-485 specifications.
- RS-485 Drive: A total of 32 transmitters and receivers allowed on one line.
- Receiver Input Sensitivity: ±200 mV, differential input.
- Input Common Mode Voltage: -7V to +12V.
- Transmitter Output Drive Capability: 60 mA (100 mA short-circuit current capability).
- Serial Data Rates: 50 to 115,200 baud. Asynchronous.
- Address: Continuously mapable within 000 to 3FF (hex) range of AT bus addresses.
Environmental
- Operating Temperature Range: 0° to +60°C
- Storage Temperature Range: -50°C to +120°C.
- Humidity: 5% to 95%, non-condensing
Power Required
- +5 VDC: 180 mA, 900 mW.
- +12V: 50 mA, 600 mW.
- -12V: 65 mA, 780 mW.
Size:
- 6.5″ long. (165 card length)
Slot
- Although designed for any AT slot, if installed in an XT-style slot then IRQ10-15 will be unavailable to the card.
Regulatory Compliance
- This product is in full compliance with CE requirements.
| Model | Description | Price (USD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COM-2S | 2 port, ISA Bus RS-232/422/485 Communications Card | $269.00 | |
| COM-1S | 1 port, ISA Bus RS-232/422/485 Communications Card | $169.00 |

